Volumetric Fluid Flow Estimation
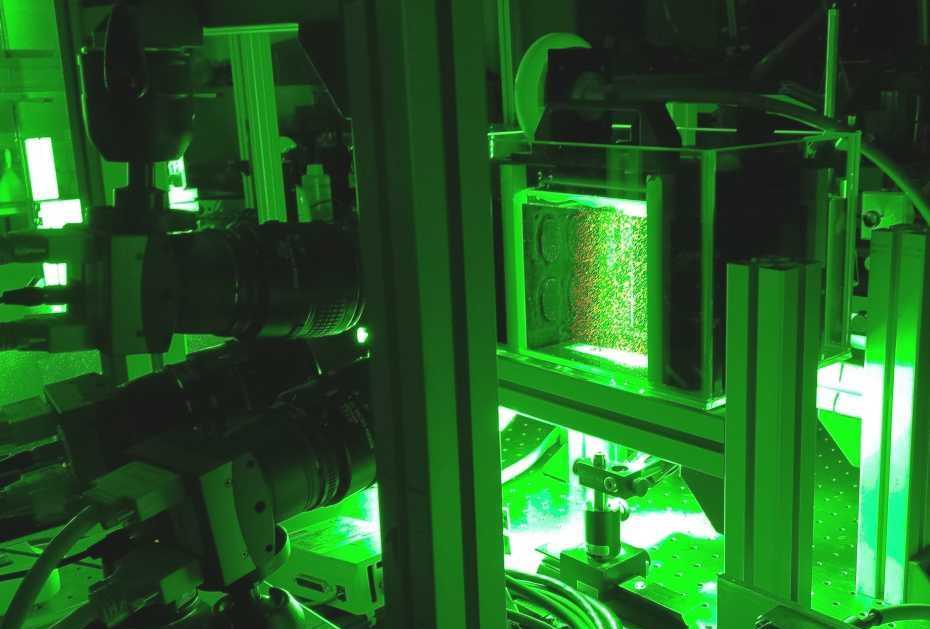
The aim of this project is to estimate the flow of a fluid seeded with tracer particles. The standard setup for volumetric flow estimation consists of an illuminated measurement volume, containing a particle-induced fluid, and three to six high-speed cameras observing the volume. From those multiple 2D observations at two or more time steps, we want to obtain a dense 3D motion field of the fluid. Applications for volumetric fluid flow estimation include experimental fluid dynamics, aero- and hydrodynamic measurements in automotive or aeronautic industries and behavioral studies about aquatic organisms or insects in turbulent flows.
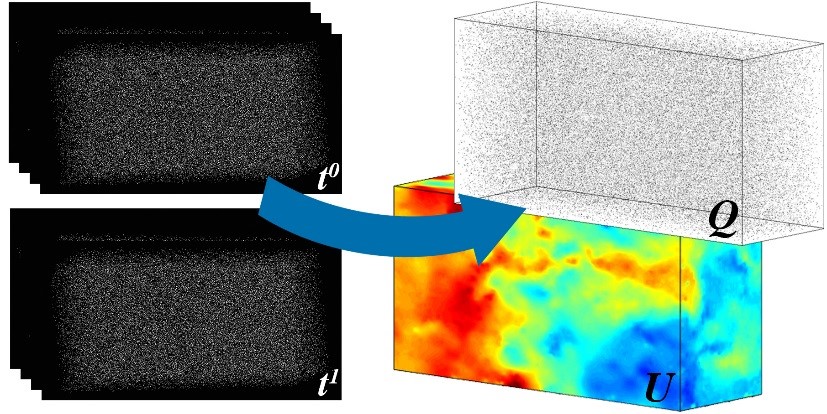
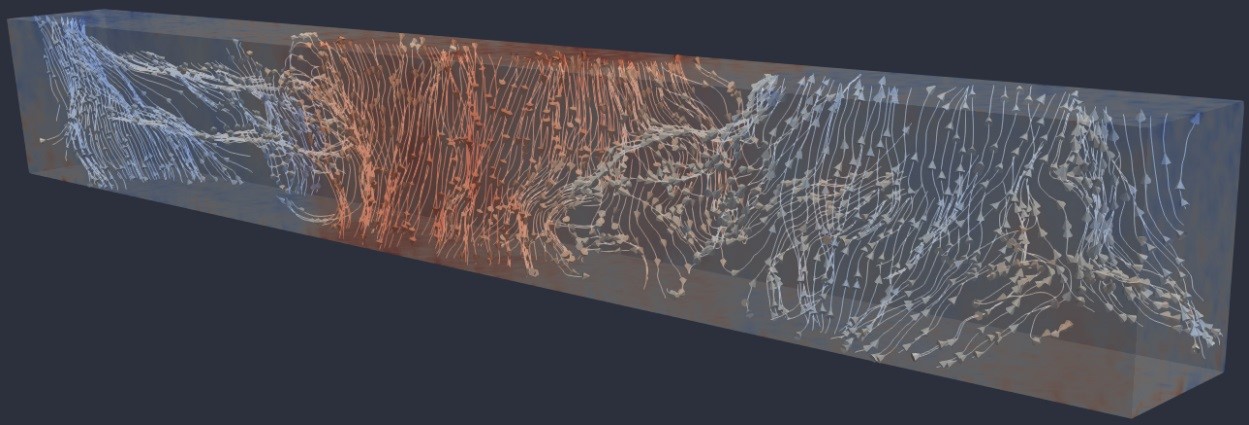
To tackle the 3D motion problem between two consecutive time steps from reconstructed particle volumes, we used a variational 3D optical flow formulation and incorporated physical constraints derived from the stationary Stokes equations in our optimization [1]. In order to handle large measurement volumes at high particle densities efficiently, we moved from a voxel-based to a sparse particle representation and introduced a new sparse descriptor [2]. Performance improved significantly when moving to a joint energy formulation for both sparse particle reconstruction and dense motion estimation [3]. Further steps we want to tackle are optimization over multiple time steps and integration of more complex camera models that can handle the multimedia setup (water-glass-air) for experiments with liquids.
Selected Publications:
[1] Lasinger K., Vogel Ch., Schindler K.: Volumetric Flow Estimation for Incompressible Fluids using the Stationary Stokes Equations (PDF, 2.3 MB), International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017.
[2] Lasinger K., Vogel C., Pock T., Schindler K.: external pageVariational 3D-PIV with sparse descriptorscall_made, Measurement Science and Technology , 2018 to appear.
[3] Lasinger K., Vogel Ch., Pock T., Schindler K.: external page3D Fluid Flow Estimation with Integrated Particle Reconstructioncall_made, arXiv:1804.03037, 2018.
Contact:
Katrin Lasinger